1.3 balance measurement planning
Measurement process planning includes measurement point determination, measurement cut-in segment planning, and measurement cut-out segment planning. In order to ensure the correctness of the machining allowance measurement, the cutting tool must be cut into the workpiece along the normal direction of the surface of the part.
2 Process planning
2.1 Cut-in section and cut-out section planning
When cutting different workpieces, the cutting and cutting modes of the cutters may be different. The common cutting and cutting directions are normal, tangential and oblique, which can be determined according to the starting position, the ending position and the geometry of the adjacent surface of the surface to be machined. Properly planning the cutting and cutting direction can prevent or reduce the impact of the cutting and cutting of the workpiece.
2.2 Cutting section planning
When the blank manufacturing precision is low (for example, the machining allowance is large, the eccentricity is large, the curvature is large, or the margin is not uniform, etc.), when machining by CNC, if it is processed according to the conventional method, the tool may be damaged or even processed. In this case, several special types of processing methods can be used.
(1) Variable feed cutting: When the tool enters the cutting section, the feed rate is gradually increased. This method is used when the eccentricity of the blank is large.
(2) Cross-cutting of the step: After the current step has finished a certain knife, it will jump to the next step for cutting. After completing the next step, continue to complete the unfinished step of the current step. Repeatedly. In this method, the processing of the workpiece with a large curvature of the contour and the uneven machining allowance is used.
(3) Multiple-passing cutting: When multiple passes, the cutting point of the tool and the position of the cutting point are variable to prevent the tool from being overcut at the point of entry or at the cutting point. This method is used when the machining allowance of a certain part is particularly large.
(4) Constant line speed cutting: For example, when the web is cut, if the spindle speed does not change, the cutting speed varies greatly throughout the tool path stroke. Cutting with constant line speed is the ideal solution.
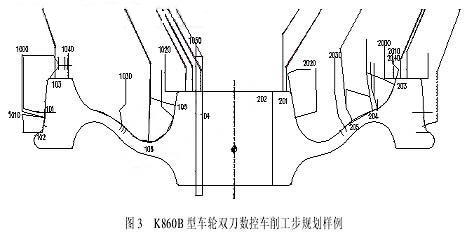
Figure 3 shows the results of planning the K860B wheel using the above-mentioned work planning principles and planning methods. In the figure, the dotted line is the advance and retraction trajectory. The data such as "1010" is the current step identification code.
2.3 Selection of feed rate and determination of cutting speed
The feed rate is usually chosen based on experience. In roughing, the feed is selected based on the material being processed, the tool holder size, the workpiece diameter, and the depth of the knife. For semi-finishing and finishing, the feed rate is selected according to the workpiece material, the radius of the tool nose radius and the cutting speed according to the roughness requirements. Cutting speed is usually also selected based on experience. Rough cars often choose a lower cutting speed, and a higher cutting speed can be selected for finishing. In addition, it is necessary to comprehensively consider the processing properties of the material, the cutting performance of the tool, the working conditions and other factors to determine a reasonable cutting speed.
3 processing planning data storage
Process planning data storage is divided into three steps: storage of single step data, data storage between work steps, and integrated storage of work step data.
3.1 Storage of single step data
The process planning process is carried out in a human-computer graphical interaction mode. The work step is the basic list of processing planning and data access. The work step data consists of two parts: tool data and cutting process data. The tool data includes the tool number, tool compensation mode, etc. The cutting process data includes cutting parameters, cutting segments, cutting segments, cutting segments, and step intersections. The data structure of the work step is as follows:

Due to the large amount of work step data, the use of structure to record this information can coordinate the intrinsic link of the data.
Previous page next page
Hospital Doors ,Hospital Room Door,Hospital Patient Room Doors,Operating Room Doors
Foshan QI'AN Fireproof Shutter Doors Co., Ltd , https://www.fsqianfiredoor.com
