ã€Abstract】 This paper describes the principle of cellulase reduction and analyzes various factors affecting the reduction rate of bio-polishing. The results show that the reduction rate of bio-polishing finishing and CMCase, mechanical stirring method and cellulose fiber fabric The materials are closely related and provide guidance for the application of textile cellulase.
With the development of modern biotechnology, the application of cellulase in the textile industry has been highly concerned by the people in the textile dyeing and finishing and bioengineering circles. At the same time, the biological enzymes have little environmental pollution, which is conducive to ecological and environmental protection, and is in line with national industrial development policies and directions. Cellulose fiber fabrics are treated with cellulase to remove surface fibers, anti-pilling, bio-polishing, stonewashing, and soft handfeel. Due to the diversified development of raw materials, fabrics can be composed of different types of raw materials, or can be composed of different types of raw materials of the same kind, such as a variety of cellulose fibers to produce fabrics by blending and interlacing; The specificity of each enzyme component of the enzyme preparation on the fiber aggregation structure, so that the enzyme has different action characteristics on different cellulose fibers. Therefore, understanding the characteristics of cellulase reduction has practical significance for actual production. In this experiment, the results of the enzyme activity determination methods of the two substrates were compared, and various factors affecting the reduction rate of the bio-polishing finishing were analyzed to provide a basis for the correct use of the cellulase.
1 experiment
1.1 Experimental reagents and materials
DNS reagent (self-matching), glacial acetic acid, sodium acetate for analytical grade, sodium carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC) as reagent grade, Xinhua qualitative filter paper, cellulase Suh0ngCellishL (Novozymes), cellulase MEGAJ2 (Shanghai Sheng Star Auxiliary), Cellulase DH-1 (self-matching), original enzyme Cellus0ftJZ (Shanghai Junheng Bio), pure cotton cloth, ramie semi-bleaching cloth, linen semi-rinsing cloth (Yager printing and dyeing).
1.2 Experimental instruments
Electronic balance, HHS electric thermostatic water bath, UV-7504 UV spectrophotometer, 6050 vacuum drying oven, PHSJ-4A laboratory pH meter, XH? KG55C oscillating water bath.
1.3 bio-polishing process
Cellulase (depending on the requirements), temperature 50 ° C, bath ratio 15:1, pH 5.0 (acetate buffer adjustment), treatment time 50 min, then 80 ° C hot water wash 10 min inactivation.
1.4 Determination of enzyme activity
It was determined by CMC enzyme activity and filter paper enzyme activity. Enzyme activity definition: Under the reaction conditions, the amount of enzyme producing 1 mM glucose per minute of substrate is 1 unit (IU) of enzyme activity.
1.5 reduction rate
The samples before and after the cellulase treatment were dried in an oven at 105 ° C to a constant weight.
Reduction rate = (after M treatment before M treatment) / M before treatment X100
2 experimental results and discussion
2.1 Determination of cellulase activity
Four cellulases of Suh0ngCellishL, MEGAJ2, DH-1 and Cellus0ftJZ were selected and tested for enzyme activity by CMC enzyme method (CMCase) and filter paper enzyme method (FPase). The results are shown in Table 1.
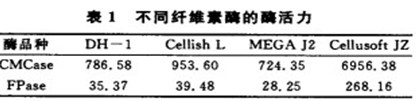
From the results of Table 1, it can be seen that the order of size of CMCase and FPase is: Cellus0fiJZ>CellishL>DH-1>MEGAJ2. Among them, CMCase mainly characterized the activity of endonuclease (EG, Cx) in cellulase system, and FPase characterized the total cellulase activity in cellulase system. Because the reaction substrates are not the same, there is no significant correspondence and comparability between the two test methods for enzyme activity. The content of the original enzyme in the cellulase is generally not more than 20%, so the enzyme activity of the original enzyme is generally much larger than that of the enzyme.
2.2 Effects of physical reduction and chemical reduction
From the current reduction of cellulose-treated cellulosic fabric formation, the reduction can be divided into chemical reduction and physical reduction. The chemical reduction is that cellulase catalyzes the hydrolysis of cellulose into glucose to reduce the fabric, while physical reduction The amount is a reduction caused by non-chemically catalyzed hydrolysis (surface fiber stripping). As can be seen from Fig. 1, from the viewpoint of the reduction rate, the mechanical action obtained by adding the glass beads to the oscillating water bath is the best, and the glass rod and the glass beads are stirred second, and the reduction rate without mechanical action is very small. Since the reduction in enzyme finishing is synergistically formed by chemically catalyzed hydrolysis and mechanical agitation, chemical reduction promotes the formation of physical depletion, which in turn causes the formation of catalytic sites for new cellulases. After the addition of the stirring medium, the dynamic boundary layer and the diffusion boundary layer on the surface of the fabric are thinned due to the irregular movement, and the enzyme molecules are easily accessible and adsorbed on the surface of the fiber, and the hydrolyzed product also accelerates dissolution. The reason why the glass rod stirring reduction rate is smaller than the water bath shaker reduction rate is mainly that the manual stirring has no continuity and continuity ( stirring for 5 min every 5 minutes). Therefore, the following research uses a water bath shaker and glass beads as a mechanical stirring device.
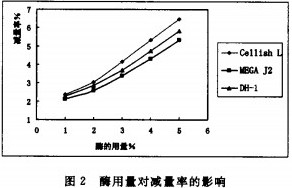
2.3 The effect of enzyme dosage on the reduction rate
The cotton fabrics were bio-polished by CellishL, MEGAJ2 and DH-1. The relationship between the amount of different enzymes and the reduction rate is shown in Fig. 2. When the enzyme dosage is 1 to 5, the average of the corresponding reduction rates is, CellishL: MEGAJ2: DH-1 = 1: 0.82: 0.86, which is the ratio of CMCase to different enzymes (CellishL: MEGAJ2: DH-1=1:0.77:0.83) is similar, indicating that under the same mechanical action, the fabric reduction rate is significantly correlated with CMCase, and EG enzyme plays a decisive role in the bio-polishing finishing of fabrics. Therefore, in bio-polishing finishing, CMCase is one of the important basis for fabric finishing effects.
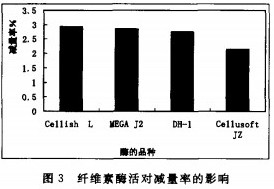
2.4 The effect of cellulase activity on the reduction rate
The Cellish L, DH-1, and Cellus0ft enzymes were live diluted to approximately the same level as the MEGAJ2 enzyme activity. The cotton fabric was then treated with 2 enzyme amounts, and the reduction rate is shown in Fig. 3. Under the same mechanical action, the reduction effects of the first three complex enzymes are basically the same, indicating that the CMC enzyme activity determines the fabric reduction rate, and the cellulose endonuclease plays a major role. The original enzyme without chemical additives has a lower reduction rate than the complex enzyme, and the chemical added reagent mainly contains a stabilizer, a surfactant and an antibacterial agent. These chemicals (such as NaCL) can significantly increase the activity of the enzyme during the finishing process; at the same time, the enzyme can be easily desorbed and moved to other binding sites to improve the fabric reduction effect. Therefore, in the compound enzyme-treated fabric, it is the result of the combined action of cellulase and chemical reagents.
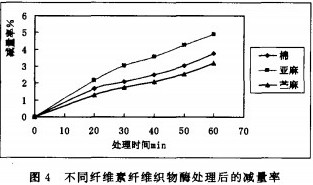
2.5 Reduction characteristics of different cellulose fiber fabrics
The cotton, linen and ramie fabrics were treated with 2DH-1 enzyme respectively, and the reduction characteristics after treatment are shown in Fig. 4. It can be seen from Fig. 4 that the flax reduction rate is the highest, mainly because the flax fabric has more fluff on the surface, and the enzyme treatment makes it easy to break off; the ramie is lower than other fibers, and the fiber has higher crystallinity in structure. The degree of orientation is related to the low porosity. In the actual process, the reduction in short time has practical reference value, and the order of reduction of these fabric varieties is: linen > cotton > ramie.
3 conclusions
3.1 The reduction of cellulase finishing is formed by the synergistic combination of chemical catalytic hydrolysis and mechanical agitation, which is the combined result of physical reduction and chemical reduction.
3.2 Under the same mechanical action mode, the reduction rate of cellulose fiber fabric is significantly correlated with CMCase, and EG enzyme plays a decisive role in the bio-polishing finishing of fabric.
3.3 The reduction characteristics of different cellulosic fiber fabrics are related to the structure and properties of the fibers and the way the fabric is woven. The order of reduction of cotton, flax and ramie in a short period of time is: linen > cotton > ramie.
The small Main Controller of LED application system has the function of address editing and lamp testing. It supports Standard DMX512 signal output with test function, supporting standard DMX512 programs broadcast. It supports automatic addressing function, supporting 3-, 4- and 6- channel addressing for SM16512 driven lamps. It can be connected to the mobile phone through WIFI, and can conduct remote control on the lamp through APP. It has the function of viewing point and color palette. It supports two modes of button operation and mobile phone control. When it is in the button operation mode, the LCD screen updates the menu in real time. When the it is in control mode, the screen can update the connection status in real time. 1 red power indicator light, 1 green WIFI data indicator light, 1 green 485 signal indicator light.
Test Controller,Flicker DMX LED Test Controller,Smart LED Test Controller, DMX Module Test Controller, RGB Test Controller,LED Lighting System Test Controller,DMX512 LED Test Controller
StrongLED Lighting Systems (Suzhou) Co., Ltd. , https://www.strongledcn.com
