Beijing December 1st, according to foreign media reports, when we call or go online, billions of bits of data are transmitted through optical fiber every second. A recent experiment shows that we may be able to "bend" light waves, thereby increasing the amount and distance of data transmitted. In this experiment, physicists used the folded laser to upload the message "Hello World" from one island to another.

The research team used a green laser beam to transmit information between the observatories on the two islands. As a result, the receiver successfully received the signal and analyzed the angular momentum that the researchers changed.
Bend photon
Humans have long used light waves to communicate. Radio is a form of light. Lasers are also very common in optical fibers. We can use the amplitude of light waves (such as AM broadcast) or frequency (such as FM broadcast), and even the phase and polarization of light waves to transmit information.
Previously, we could only incorporate information into the above four properties of light waves (also known as degrees of freedom), which limited the amount of information we use to transmit photons. A research team composed of scientists from various countries at the University of Vienna hopes to incorporate information into the fifth attribute of light waves, which is the angular momentum of light waves, which greatly increases the distance of information transmission. They achieved data transmissions between the two observatories on the Canary Islands, about 142 kilometers away.
Although it sounds counter-intuitive, light does have angular momentum. This is because the photons that make up the light actually bend and turn several times. In recent years, scientists have found ways to increase the number of photon bends, thereby changing the angular momentum of the light.
“After adding a degree of freedom, the wavelength of light is still the same as the original, but by introducing a factor of n, we have greatly increased the amount of information transmitted.†Mario Klein, PhD student at the University of Vienna and lead author of the study (Mario Krenn) pointed out. Here "n" refers to the "mode" of the angular momentum of the light wave, and can only be an integer. Assume that the modulus used when propagating the information is 5, using 10 wavelength channels, then the amount of data transmitted can be up to 5 times that of the original 10 wavelength channels.
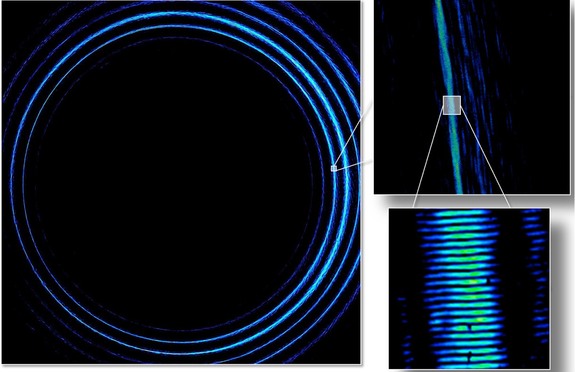
It can be seen from the photos (the color of the picture is inaccurate). When zoomed in twice, the light waves look amazingly complex.
Light propagation
In general, when a laser hits a blank screen, it will show a halo. Researchers used computers to superpose angular momentum in different ways, thereby incorporating information available for interpretation in light waves. In this way, the researchers synthesized a message that could be read as "Hello of the World."
However, being able to interpret the information is only part of the experiment. Next, scientists also need to transfer information to other places. Previously, most scientists believed that photons could not transmit information in the atmosphere, because they believed that the angular momentum could be easily affected by the refractive index of light, and the air pressure and air humidity would change the refractive index. But they are wrong. The research team used a green laser beam to transmit information between the observatories on the two islands. As a result, the receiver successfully received the signal and analyzed the angular momentum that the researchers changed. "We have been surprised that the distance can exceed 3 kilometers," said Klein.
However, scientists do not know why the information can be successfully transmitted. It may be because the previous hypothesis itself is wrong. The air does not interfere with this type of transmission.
The experiment was a complete success. In the future, people will carry out more research work and gradually apply this technology to information and communication. Klein pointed out that the transmitters and receivers used in the experiment are actually very simple. The most complicated ones are the processing of signals, but this can also be solved by common mathematical means.
A fingerprint is an impression of the friction ridges of all or any part of the finger.Fingerprint identification (sometimes referred to as dactyloscopy[3]) is the process of comparing questioned and known friction skin ridge impressions (see Minutiae) from fingers, palms, and toes to determine if the impressions are from the same finger (or palm, toe, etc.).based on this technology ,people conduct all kinds of products with fingerprint identification technology .like Fingerprint Lock ,which is use the fingerprint as the key to unlock the door lock .
Fingerprint Lock
Fingerprint Lock,Fingerprint Door Lock,Fingerprint Machine,Mobile Fingerprint Lock
ChangChun E-vida Technology Co.,ltd , https://www.evidatech.com
