Due to its advantages of small specific gravity, good thermal conductivity, high electrical conductivity, and corrosion resistance, aluminum alloy die forged parts are widely used in parts with medium and high strength requirements. Aluminum alloy heat forging process is characterized by poor fluidity, low plasticity, good thermal conductivity, narrow forging temperature range, strict fore and final forging temperature requirements, and the characteristics of the heating die forging is that the aluminum alloy does not produce allotropism transformation. Mainly rely on the correct control of forging mechanical parameters to improve the metal structure, so that the metal flow line is uniformly distributed along the shape of the forgings to improve the mechanical properties; the quality of the heating die forging is the aluminum alloy is easy to produce two major defects of folding and cracking. Among them, folding can reduce the bearing area of ​​the parts, and stress concentration can easily occur during service, and it becomes a source of fatigue failure, which is a great hazard. Folding waste accounts for about 70% to 80% of the total number of forging wastes; cracks are more harmful, and cracks are about to be reduced. It accounts for 5% to 10% of the total number of forging waste products.
2 Example analysis of folding and cracking
2.1 Three-way Valve Fold Analysis
The three-way valve forging shown in Fig. 1 is made of LY11 or LD10, and the blank size is φ50mm×55mm or 40mm×40mm×69mm and weighs 0.29kg, which results in folding during forging. From the forging macroscopically, it can be seen that the folding of the middle part is caused by the confluence of the two flowing metal convections, and the folding at the transition between φ23mm and the middle part is pressed into the other part by the local deformation of a part of the metal. Internally formed, there is also a rapid flow of metal to the adjacent surface metal with the formation of flow, in addition to a certain degree of oxidation at the fold.
2.1.1 Causes of Folding
The billet has a large cross-section size, the shape of the billet is unreasonable, and the partial press-in type forming has a small fillet radius at the transition between the die and the die. The amount of one-time reduction during operation is too large.
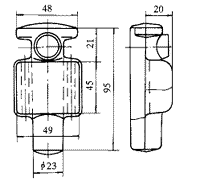
Fig. 1 Three-way valve forging
2.1.2 Method to eliminate folding The die forging inclination of the die is increased from 5° to 7°; the corner radius at the transition between the die φ23mm and the forging is increased from R3mm to R8mm; the forging is easy to fold The manufacturing direction of the part of the mold was polished in the direction of metal flow; the surface roughness of the mold was reduced from Ra = 1.6μm to Ra = 0.4μm; the size of the blank was changed to 38mm × 58mm × 74mm at the end of the forging. Forging and forming, press the light and heavy weight first, and lubricate the upper die properly.
2.2 Analysis of bearing cap cracks
As shown in Figure 2, the 492Q gasoline engine bearing cap forgings, material for the LY11 extruded bar, the blank size of φ70mm × 120mm, weight 1.3kg. When the billet is upset along the axial direction of the billet, a macroscopic oblique crack occurs in the 45° direction of the forging blank axis, and the crack opening angle is 30° to 50°.
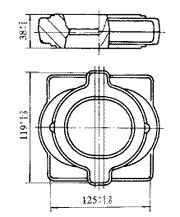
Figure 2 Gasoline bearing cap forgings
2.2.1 Causes of Cracks
Extruded aluminum bar has obvious anisotropy, in which the longitudinal mechanical properties are significantly higher than the transverse mechanical properties (longitudinal toughness and low transverse toughness). At the beginning of forging, under the condition of unequal triaxial stress or non-triaxial compressive stress, there is a large shear stress, which can easily cause the damage of grain contact between blanks, which is not conducive to the development of slip deformation, and poor deformability. And there is a crack. At the same time, due to the unequal deformation caused by the additional stress and temperature uneven thermal stress, the deformation of the large part and the deformation of the small part of the interaction, tensile stress beyond the part of the crack will occur.
2.2.2 Methods to Eliminate Cracks
Strictly control the start and end forging temperatures, reduce the number of billets installed, shorten the time from billet discharge to forging, turn the billet when it is heated for a certain period of time, and use extrusion billets with good toughness along the axial direction and good plasticity along the billets. The flattened billet is forged radially, ie perpendicular to the fiber direction, and then forged.
2.3 Analysis of Oil Plug Folding and Cracking
As shown in Fig. 3, the oil plugged forgings were made of LY11 or LY12 extruded bar stock. The blank size was φ35mm×45mm, and the weight was 0.08kg. In the RFX-45 box type electric furnace heating, each time the amount of 15 pieces, but after forging 10 pieces, using axial or radial upsetting roughing, and then the final forging, appear along the die surface direction of the flash A crack of 15° to 35° is formed and extends along the forging. When using φ30mm×60mm billet to upset the billet in the axial direction, a large fold occurs around the R10mm of the forging ring.
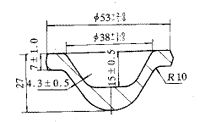
Fig. 3 Oil plugging forgings
2.3.1 Causes of Folding and Cracking
Every time the billets are discharged in excess, the initial forging temperature is low, the deformation degree of the billet during the final forging is too large or the forging ratio is too large, and the forging die is preheated or improperly lubricated.
2.3.2 Methods to Eliminate Folding and Cracking Select the billet size smaller diameter φ35mm, the billet heated to 480 °C heat 2h, each billet out of the amount of 10 or less, the final forging light and heavy after the first to improve Preheating temperature of the forging die, and lubricating the upper die once every 2 pieces.
3 Conclusion
In the actual production, the quality control of aluminum alloy die forgings folded and cracked two major quality defects should be carried out in combination with prevention, process technology and production management. The following aspects should be specifically implemented:
(1) The necessary analysis of the technical conditions of forging equipment, technological equipment and blanks shall be carried out so that the forging process is in line with the actual production and is advanced, reasonable, complete and accurate.
(2) In the design of forging dies, the forming force required by the forgings and the tonnage of the equipment should be taken into account. The volume of the blanks or intermediate blanks should be reasonably distributed. The correct filling method should be selected to increase the fillet radius at the transition of the forging dies. Or forging slope, reducing the surface roughness of the mold (including flash bridge).
(3) It should be ensured that the aluminum alloy raw materials used have no defects such as folding, cracks and coarse crystal rings. For the heating of the billet, the loading amount should be strictly controlled, the billet should be turned during half of the heating time, and the time from tapping to forging should be reduced as much as possible.
(4) During the forging operation, the principle of light weight and heavy weight shall be used to properly control the degree of deformation or hammering force of the blank, reasonably use the anisotropy of the extruded raw material, and correctly preheat the forging die and the operating tool. And reasonably lubricate forging dies (especially upper die dies).
(5) In forging production, the production squadron shall be under the unified command of the production squad leader. The first inspection shall be accompanied by competent technical personnel. If necessary, follow the class operation to guide the production. At the same time, the first batch of first production shall be arranged as far as possible in the day shift production in order to facilitate The quality defects of the forgings were found, and after confirming that there were no defects such as folds and cracks, the production could be evenly and rhythmically balanced at the specified time intervals.
(6) In the inspection of forgings, the first inspection must be carried out and the “three-inspection system†must be strictly implemented. The process inspection, intermediate inspection, touring inspection, and final inspection should also be performed to prevent system quality defects from flowing into the next process. .
Folding and Cracking Causes
Every time the billets are discharged in excess, the initial forging temperature is low, the deformation degree of the billet during the final forging is too large or the forging ratio is too large, and the forging die is preheated or improperly lubricated.
Garden Street Light,Solar Power Garden Lights,Garden Solar Light Outdoor,Solar Powered Garden Street Light
Yantai LUHAO Lighting CO.,Ltd , https://www.luhaolight.com
